7.9 KiB
Windows Forensics
Windows 10 Notifications
In the path \Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Notifications you can find the database appdb.dat before Windows anniversary or wpndatabase.db after Windows Anniversary.
Inside this SQLite database you can find the Notification table with all the notifications in xml format that may contain interesting data.
Timeline
Timeline is a Windows characteristic that provides chronological history of web pages visited, edited documents, executed applications...
The database resides in the path \Users\<username>\AppData\Local\ConnectedDevicesPlatform\<id>\ActivitiesCache.db
This database can be open with a SQLite tool or with the tool WxTCmd ****which generates 2 files that can be opened with the tool TimeLine Explorer.
Windows RecentAPPs
Inside the registry NTUSER.DAT in the path Software\Microsoft\Current Version\Search\RecentApps you can subkeys with information about the application executed, last time it was executed, and number of times it was launched.
BAM
You can open the SYSTEM file with a registry editor and inside the path SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\bam\UserSettings\{SID} you can find the information about the applications executed by each user note the `{SID}` in the path and at what time they were executed the time is inside the Data value of the registry.
Windows Mail App
This application saves the emails in HTML or text. You can find the emails inside subfolders inside \Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Comms\Unistore\data\3\. The emails are saved with .dat extension.
The metadata of the emails and the contacts can be found inside the EDB database: \Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Comms\UnistoreDB\store.vol
Change the extension of the file from .vol to .edb and you can use the tool ESEDatabaseView to open it. Inside the Message table you can see the emails.
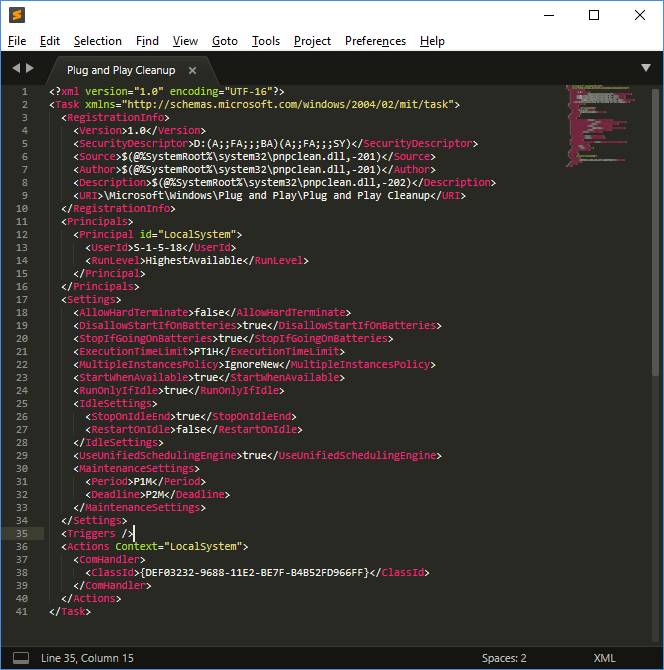
Plug and Play Cleanup
The 'Plug and Play Cleanup' scheduled task is responsible for clearing legacy versions of drivers. It would appear based upon reports online that it also picks up drivers which have not been used in 30 days, despite its description stating that "the most current version of each driver package will be kept". As such, removable devices which have not been connected for 30 days may have their drivers removed.
The scheduled task itself is located at ‘C:\Windows\System32\Tasks\Microsoft\Windows\Plug and Play\Plug and Play Cleanup’, and its content is displayed below:
The task references 'pnpclean.dll' which is responsible for performing the cleanup activity additionally we see that the ‘UseUnifiedSchedulingEngine’ field is set to ‘TRUE’ which specifies that the generic task scheduling engine is used to manage the task. The ‘Period’ and ‘Deadline’ values of 'P1M' and 'P2M' within ‘MaintenanceSettings’ instruct Task Scheduler to execute the task once every month during regular Automatic maintenance and if it fails for 2 consecutive months, to start attempting the task during.
This section was copied from here.
Windows Store
The installed applications can be found in \ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\AppRepository\
This repository has a log with each application installed in the system inside the database StateRepository-Machine.srd.
Inside the Application table of this database it's possible to find the columns: "Application ID", "PackageNumber", and "Display Name". This columns have information about pre-installed and installed applications and it can be found if some applications were uninstalled because the IDs of installed applications should be sequential.
It's also possible to find installed application inside the registry path: Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Appx\AppxAllUserStore\Applications\
And uninstalled applications in: Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Appx\AppxAllUserStore\Deleted\
Windows Events
Information that appears inside Windows events:
- What happened
- Timestamp
- Users involved
- Hosts involved
hostname, IP - Assets accessed
files, folder, printer, services
The logs are located in C:\Windows\System32\config before Windows Vista and in C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs after Windows Vista.
Before Windows Vista the event logs were in binary format and after it, they are in XML format and use the .evtx extension.
The location of the event files can be found in the SYSTEM registry in HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\EventLog\{Application|System|Security}
They can be visualized from the Windows Event Viewer **`eventvwr.msc`** or with other tools.
Security
These event register the accesses and give information about the security configuration.
they can be found in C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Security.evtx.
The max size of the event file is configurable, and it will start overwriting old events when the maximum size is reached.
Events that are registered:
- Login/Logoff
- Actions of the user
- Access to files, folders and shared assets
- Modification of the security configuration
Events related to the user authentication:
| EventID | Description |
|---|---|
| 4624 | Successful authentication |
| 4625 | Authentication error |
| 4634/4647 | log off |
| 4672 | Logon with admin permissions |
Inside the EventID 4634/4647 there are interesting sub-types:
- 2 (interactive): The login was interactive using the keyboard or software like VNC or
PSexec -U- - 3 (network): Connection to a shared folder
- 4 (Batch): Process executed
- 5 (service): Service started by the Service Control Manager
- 7: Screen unblocked using password
- 8 (network cleartext): User authenticated sendin clear text passwords. This event use to come from the IIS
- 9 (new credentials): It's generated when the command
RunAsis used or the user access to a network service with different credentials. - 10 (remote interactive): Authentication via Terminal Services or RDP
- 11 (cache interactive): Access using the last cached credentials because it wasn't possible to contact the domain controller
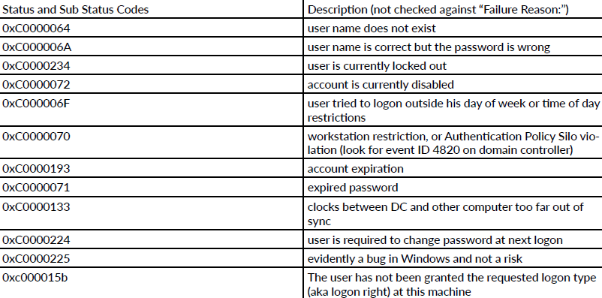
The Status and sub status information of the event s can indicate more details about the causes of the event. For example take a look to the following Status and Sub Status Codes of the Event ID 4625:
Recovering Windows Events
It's highly recommended to turn off the suspicious PC by unplugging it to maximize the probabilities of recovering the Windows Events. In case they were deleted, a tool that can be useful to try to recover them is Bulk_extractor indicating the evtx extension.
Identifying Common Attacks with Windows Events
Brute-Force Attack
A brute-force attack can be easily identifiable because several EventIDs 4625 will appear. If the attack was successful, after the EventIDs 4625, an EventID 4624 will appear.
Time Change
This is awful for the forensics team as all the timestamps will be modified.
This event is recorded by the EventID 4616 inside the Security Event log.
USB devices
The following System EventIDs are useful:
- 20001 / 20003 / 10000: First time it was used
- 10100: Driver update
The EventID 112 from DeviceSetupManager contains the timestamp of each USB device inserted.
Turn Off / Turn On
The ID 6005 of the "Event Log" service indicates the PC was turned On. The ID 6006 indicates it was turned Off.
Logs Deletion
The Security EventID 1102 indicates the logs were deleted.